The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
Quantity exchanged price floor.
At equilibrium the quantity demanded is 700 units.
There are units that are socially efficient to trade but aren t traded because their value is less than the price floor.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low.
The quantity demanded at the price ceiling will equal the quantity supplied.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists.
A price floor example.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
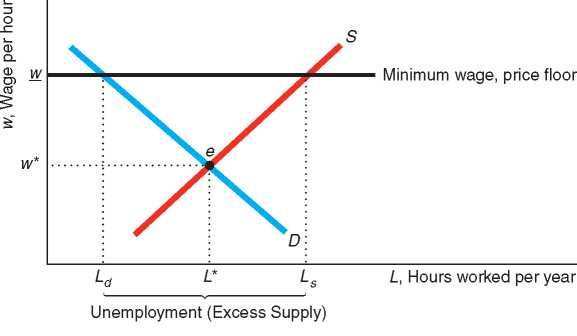
In figure 5 5 a price floor the price floor is illustrated with a horizontal line and is above the equilibrium price.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Minimum wage and price floors.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
At the price floor the quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied which is a surplus situation.
A price floor is only effective when set above the equilibrium price below left.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
The amount exchanged in the market will be limited by the smaller of the two quantities q d in this case.
The quantity demanded at the price ceiling will equal the quantity.
Price and quantity controls.
Consequently at the price floor a larger quantity is supplied than is demanded leading to a surplus.
At the price ceiling there is a surplus of orange juice.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
The quantity supplied at the price ceiling will equal the quantity exchanged.
When the price floor is set below the equilibrium.
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling.