Porous materials are a group of substances with moderate density great distinct surface and a variety of unusual characteristics in the physical automatic and acoustical fields.
Porous ceramic example of porous materials.
Often overlooked are details such as the material surface texture.
A ceramic is any of the various hard brittle heat resistant and corrosion resistant materials made by shaping and then firing a nonmetallic mineral such as clay at a high temperature.
For example porous piezoelectric ceramics show good piezoelectric property and are expected to be used for ultrasonic transducers etc.
Some of the more common porous surfaces include laminate granite and various types of tile and plastic materials.
Hard surfaces are a combination of porous and nonporous materials.
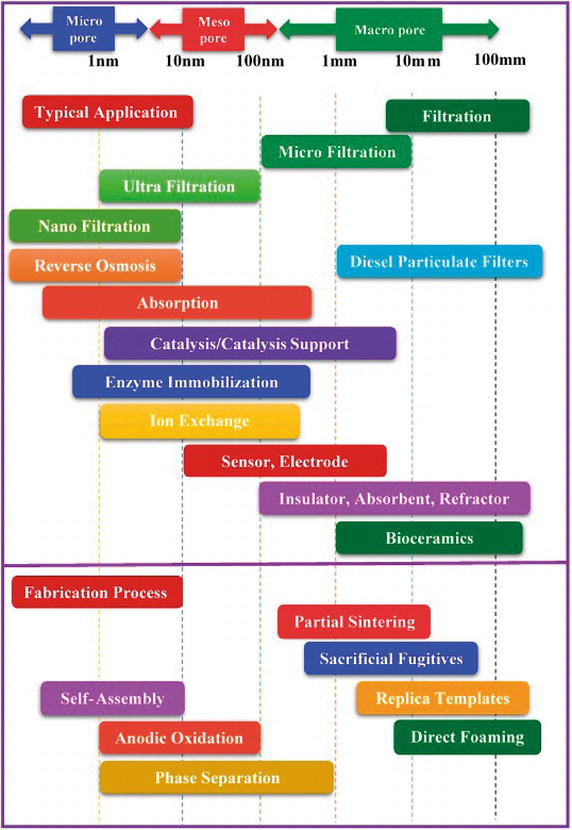
Combining tightly toleranced pores with unique ceramic material properties enables applications not feasible before.
Hard plastic like bakelite tightly spaced c.
Paper cardboard sponges pumice stones untreated wood and cork are a few examples of porous materials.
23 a variety of porous ceramics have been applied as materials for refractory bricks of kilns and furnaces in various industrial fields due to their low thermal conductivity and high thermal shock.
If you soak them in water mixed with red ink you will never get all the ink out.
Porous ceramics are often used for chemical filtration and fluid separation.
Common hard surface materials are stainless steel solid surface laminate porcelain and a wide variety of tile and ridged plastic materials.
Sponge is an obvious example of porous material.
For example porous piezoelectric ceramics show good piezoelectric property and are expected to be used for ultrasonic transducers etc.
Common examples are earthenware porcelain and brick.
23 a variety of porous ceramics have been applied as materials for refractory bricks of kilns and furnaces in various industrial fields due to their low thermal conductivity and high thermal shock.
In this book we focus on metals ceramics and glasses.
The crystallinity of ceramic materials ranges from highly oriented to semi crystalline vitrified and often completely amorphous e g glasses.
These materials composed of at least two phases like solid ceramic phase and the gas filled porous phase the gas content of these pores usually regulates itself to the environment as an exchange of gas with the environment is possible through pore channels.
Porous ceramics are categorized as those ceramics having high percentage porosity between 20 and 95.
Custom coorstek porous ceramics can be tailored from 0 1 100 µm with precision tolerances and a variety of ceramic material options.
The comparison of porous materials with respect to some specific properties is listed in table 1 3.